User guide
The data cubes can be used to explore a range of clinical data related to hospital separations. This document will provide some tips on how to utilise the data cubes generally and how to deal with the different formats in which the cubes are provided.
For older years, hospitals data cubes are available in the SAS cubes software. Hospitals data cubes have been made available in excel format in more recent years. The guide for extraction of information from these cubes depends on the format in which they are available.
Hospitals data cubes in Excel
The excel data cube workbooks consist of two sheets:
- DRG Counts Data contains separation statistics by DRG by age group by sex by same-day status.
- DRG Counts Summary contains a pivot table showing separation statistics by DRG. This pivot table can be modified to various levels by right clicking on the table, selecting ‘Show Field List’, and then modifying the pivot table as desired (see Figure 1).
- Variables in the ROWS list can be removed to disaggregate at higher levels.
- Variables such as age group, sex and/or same-day flag can be dragged to the COLUMNS list to disaggregate by these variables.
Figure 1: DRG counts summary pivot table
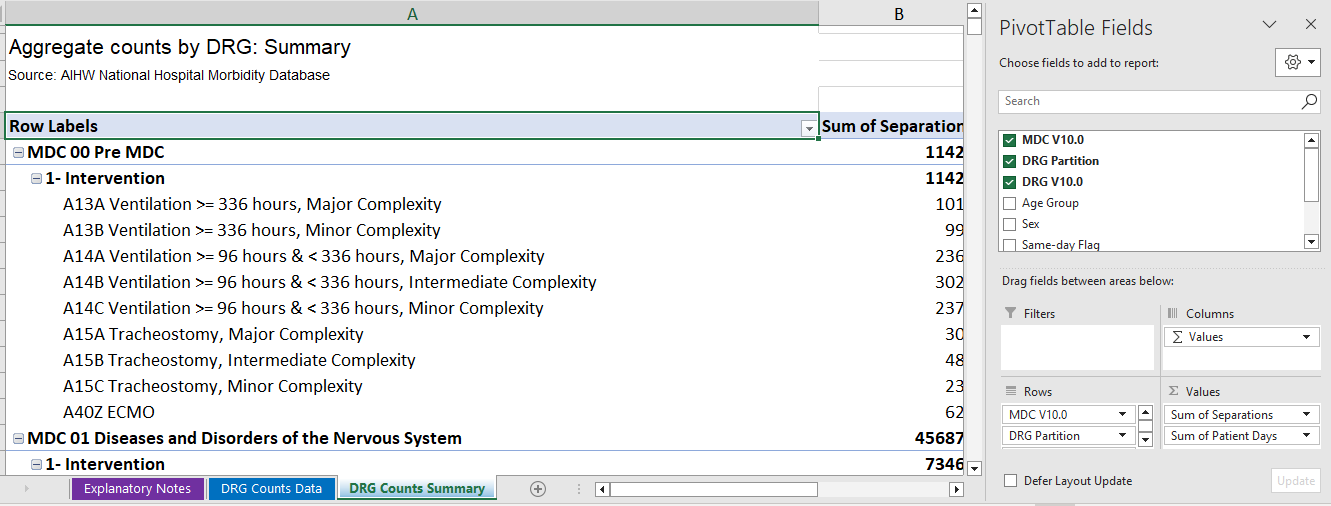
Source: DRG data cube, 2021-22, classified using AR-DRG version 10.0.
The cubes contain information on the number of separations and number of patient days. Once the cube has been aggregated/disaggregated to the desired level, average length of stay can be calculated as number of patient days/number of separations.
Hospital data cubes in SAS
These data cubes will open in a new window. Data will be displayed at the most aggregated level, as in Figure 2:
Figure 2: Data cube aggregate view
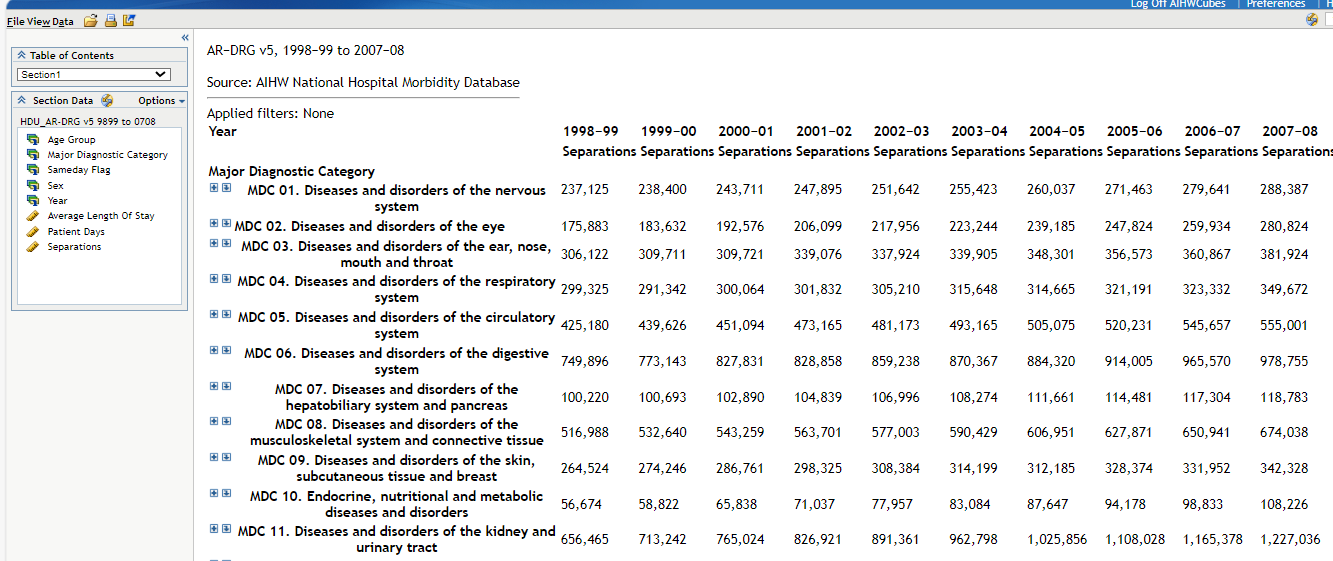
Source: DRG data cube, 1998-99 to 2007-08 classified using AR-DRG version 5.0/5.1.
Expanding categories and sub-categories
Clicking on the plus (+) symbols against each row will expand that item into its relevant sub-categories, within the current view.
Clicking the arrow symbols beside the plus will expand the category and also limit the view to just that expanded area of interest.
Right clicking on category headings such as MDC will bring up a menu where you can click ‘Expand All’, which will expand every item in that list (see Figure 3). If you also do this with the partition headings, you can expand out the entire data cube and display all of the available information.
Figure 3: Expand data cube Major Diagnostic Categories
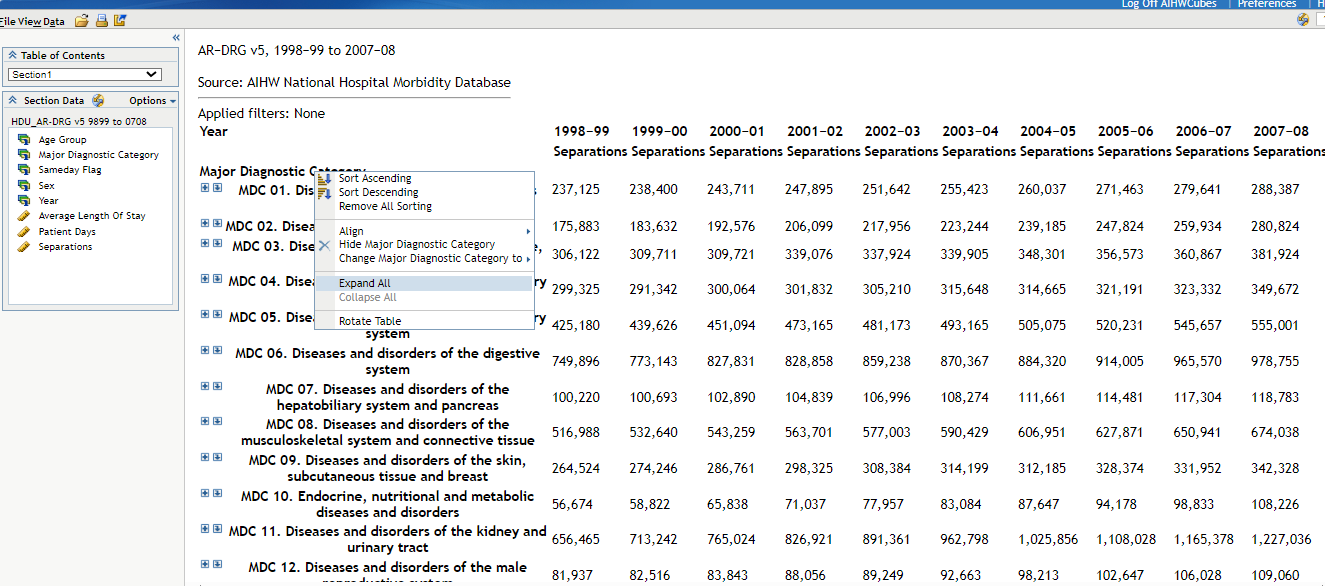
Source: DRG data cube, 1998-99 to 2007-08 classified using AR-DRG version 5.0/5.1.
Adding breakdowns
In the default view, the cube will just present the number of hospital separations by year but you can also add other breakdowns such as by Age group and sex and include patient days or average length of stay.
To add an extra breakdown, right click on one of the numbers in the cube and choose ‘Assign data’ (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Assign data option
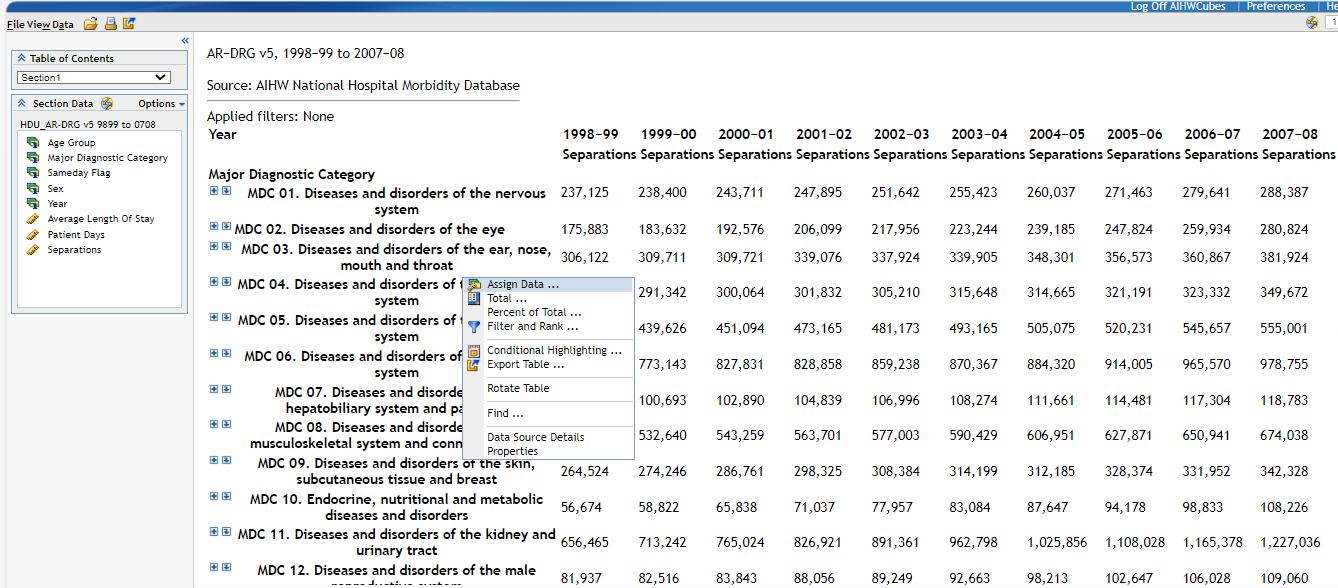
Source: DRG data cube, 1998-99 to 2007-08 classified using AR-DRG version 5.0/5.1.
Then choose which variables to add to rows or columns of the cube (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Assigning data
Source: DRG data cube, 1998-99 to 2007-08 classified using AR-DRG version 5.0/5.1.
Exporting data to Excel
The current view of the data cube can easily be exported to Excel by choosing ‘Export…’ from the ‘File’ menu, and then saving the file to your computer. The cube will be extracted in an old version of excel in .xls format. The export can be opened by choosing yes if the following dialogue box appears:
Exporting the whole data cube
To do this, first see the notes about Expanding the categories and sub categories first and using Expand All. Then once you have the full view of the cube, export the data as per the step above.
Tips on using the AR-DRGs data cube
Note that the use of the different AR-DRG versions in the data cubes over time means that data across years may not be exactly comparable.
Within the cubes, users can view the AR-DRG by working down from the Major Diagnostic Category (MDC) level to the Partition of the MDC to the individual DRGs, as outlined below.
- Major diagnostic category
- Partition (Intervention/Medical for AR-DRG versions 9.0 and later, Surgical/Medical/Other for earlier DRG versions)
- AR-DRG
- Partition (Intervention/Medical for AR-DRG versions 9.0 and later, Surgical/Medical/Other for earlier DRG versions)
For example under AR-DRG 10.0
- MDC 04. Diseases and disorders of the respiratory system
- Intervention
- AR-DRG E01A Major Chest Interventions, Major Complexity.
- Intervention
Users of the data cube are likely to require some familiarity with AR-DRGs and have access to the definitions manual and can also refer to the Australian Hospital Statistics publications. Users will generally need to know what MDC the information they are looking for is in, to work down to more specific levels of detail. More information about the breakdowns and categories used within the data cube are given below.
Major diagnostic categories (MDCs)
The data cube is categorised by the Major Diagnostic Categories (MDCs) into which the patient’s diagnosis and the associated AR-DRG falls. They correspond generally to the major organ systems of the body. Below is a list of each of the MDCs and the range of AR-DRGs that fall into each category under AR-DRG version 10.
MDC | MDC Description | AR-DRG beginning with |
|---|---|---|
Pre-MDC | Major procedures where the principal diagnosis may be associated with any MDC | A |
01. | Diseases and disorders of the nervous system | B |
02. | Diseases and disorders of the eye | C |
03. | Diseases and disorders of the ear, nose, mouth and throat | D |
04. | Diseases and disorders of the respiratory system | E |
05. | Diseases and disorders of the circulatory system | F |
06. | Diseases and disorders of the digestive system | G |
07. | Diseases and disorders of the hepatobiliary system and pancreas | H |
08. | Diseases and disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | I |
09. | Diseases and disorders of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and breast | J |
10. | Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases and disorders | K |
11. | Diseases and disorders of the kidney and urinary tract | L |
12. | Diseases and disorders of the male reproductive system | M |
13. | Diseases and disorders of the female reproductive system | N |
14. | Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium | O |
15. | Newborns and other neonates | P |
16. | Diseases and disorders of the blood and blood forming organs and immunological disorders | Q |
17. | Neoplastic disorders (haematological and solid neoplasms) | R |
18. | Infectious and parasitic diseases | T |
19. | Mental diseases and disorders | U |
20. | Alcohol/drug use and alcohol/drug induced organic mental disorders | V |
21A. | Injuries, Poisoning and Toxic Effects of Drugs: Multiple Trauma | W |
| 21B. | Injuries, Poisoning and Toxic Effects of Drugs | X |
22. | Burns | Y |
23. | Factors influencing health status and other contacts with health services | Z |
| GIs unrelated to principal diagnosis | General interventions unrelated to principal diagnosis | 8 |
Error-DRGs | Error DRGs | 9 |
Broad categories of service
The data cube is next broken down by the partitions of the AR-DRG. These partitions represent the broad category of service associated with that AR-DRG, as described below:
For AR-DRG versions 8.0 and earlier:
- Surgical: separations for which the AR-DRG belonged to the Surgical partition of the AR-DRG classification (involving at least one operating room procedure).
- Medical: separations for which the AR-DRG belonged to the Medical partition (not involving an operating room procedure or a locally significant non-operating room procedure).
- Other: separations for which the AR-DRG did not belong to the Surgical or Medical partitions (involving no operating room procedures but at least one non-operating room procedure significant to the MDC, such as endoscopy).
For AR-DRG versions 9.0 and later:
- Intervention: separations for which the AR-DRG belonged to the Intervention partition (involving a General Intervention (operating room procedure) or at least one Specific Intervention (non-operating room procedure) significant to the MDC).
- Medical: separations for which the AR-DRG belonged to the Medical partition (not involving an operating room procedure or a locally significant non-operating room procedure).


